By Edu Abade
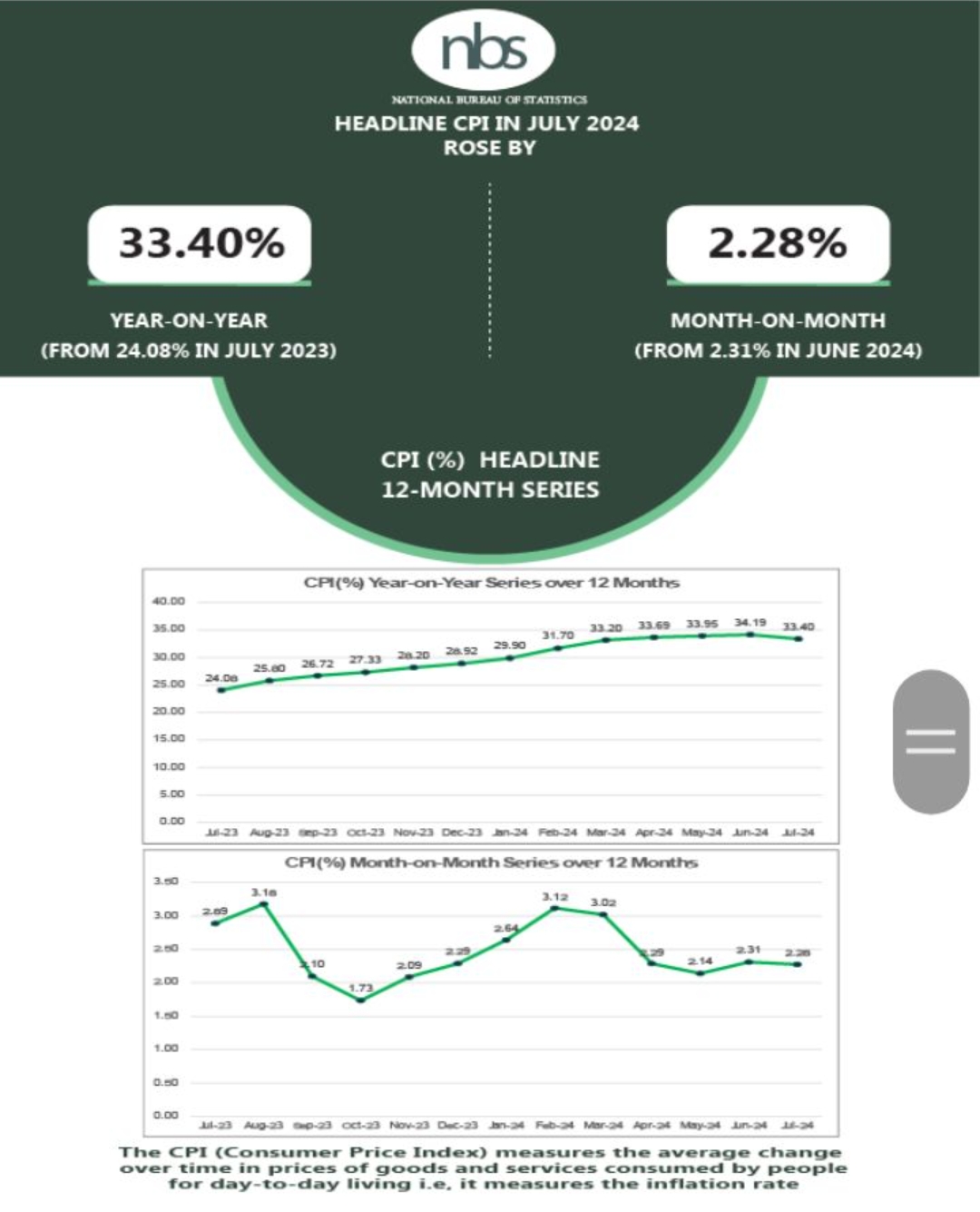
Headline inflation rate eased slightly to 33.40 percent in July 2024, representing a 0.79 percentage point decline from the 34.19 recorded in June 2024.
The latest National Bureau of Statistics’ (NBS) CPI and inflation report also revealed that the food inflation rate dropped from 40.87 percent in June 2024 to 39.53 percent in July 2024, a decrease by 1.34 percentage point. This is the first decline in the inflation rate in 19 months.
Despite being the first, the decline is a positive sign for economic stability, indicating that efforts to control inflation may be beginning to take effect. State-wise, inflation levels did not ease in all states, as many northern states witnessed an increase in inflation.
The Centre for the Study of the Economies of Africa (CSEA) projects that as the harvest season commences, food inflation is expected to ease further, which in turn is expected to reduce headline inflation.
It expressed concern that supply constraints, foreign exchange uncertainty and rising gasoline prices are ongoing concerns that could hinder the further decline in the inflation rate.
“Hence, it is pertinent for the government to invest in agricultural infrastructure and technology to boost local food production. The government introduced the duty-free window for essential food items to tame food inflation in early July. The Nigeria Customs Service (NCS) said the policy would be implemented from mid-July to December 31.
“The government should ensure that the policy does not adversely affect domestic food production. In addition to the duty-free policy, the central bank should strengthen foreign exchange reserves to ensure currency stability. Exchange rate pass-through is lower when the currency is stable, reducing the contribution of imported inflation in headline inflation,” it stated.









